How Are Ear Vegetations Treated In Children?
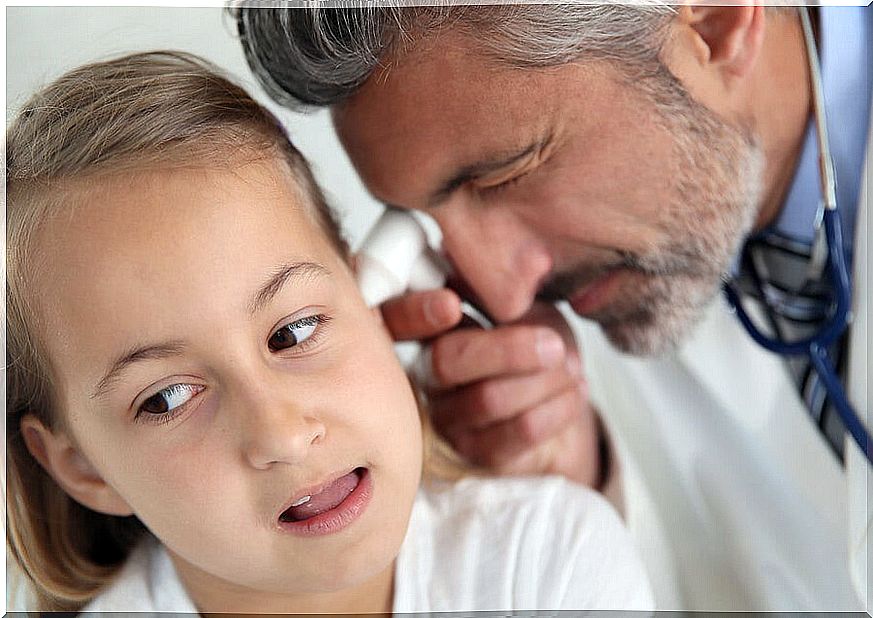

Ear growths in children, also known as adenoids, are a patch of tissue located high in the throat, behind the nose . Together with the tonsils, they form the upper axis of the lymphatic system, whose tasks include eliminating infections.
These tissues begin to grow as soon as the baby is in gestation inside the mother’s womb . During the first six years of life, they are responsible for trapping all germs and bacteria that enter the body through the mouth and nose.
Once this stage is completed, the human body uses other defense methods. For this reason, under normal conditions, the vegetation gradually decreases in size. By adolescence, it should be completely gone.
The origin of vegetations
These types of vegetations generate lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell present in the blood. When they go into action, it is common for the vegetations of the ears in children to swell and cause a problem also called hypertrophic adenoids.
Signs that something is wrong with the adenoids
These tissues are commonly very active in children between the ages of three and six. During this stage, the immune system is finishing its development; too much work can cause them to remain swollen, even when they do not have an infection.
It is in this scenario that the greatest difficulties tend to arise . A vicious circle is generated that, sometimes, cannot be broken with simple medication.
Swollen adenoids do not allow proper air circulation, leading to infections. Infections that do not yield to antibiotics end up causing swelling, which in turn hinders air flow.

Other symptoms
- Difficulty breathing: patients who are affected usually do it through the mouth, since the transit of oxygen through the nostrils is seriously hampered. This, in turn, leads to bad breath, general dry mouth, chapped lips and a ‘nasal voice’.
- Sleep disturbances, with episodes of apnea: there may be a total interruption of breathing for a few seconds, while the child remains asleep. Snoring appears, sounds that are proportional to the degree of obstruction.
- The abundant nasal mucus is another of the frequent signs, as well as difficulty to ingest solid foods and even liquids. The most persistent cases can become deformities of the hard palate and the dental arch; this, in turn, increases the risk of deficit bite disorders.
Vegetations of ears in children and otitis
Repeated episodes of otitis are a constant in children with continued adenoid hypertrophy. It is necessary to take extreme precautions, because it is a relatively common situation.
Otitis media, in which an inflammation of the middle ear occurs at the back of the eardrum, is the most common pathology. If the disease progresses uncontrollably, it can lead to discharge of waxy (watery), mucous, or purulent fluid (pus).
Treatment
When the vegetations of ears in children end in otitis media, a treatment with antibiotics is prescribed for a period of 10 to 12 days. If the appearance of these infections is frequent, the specialists go to the next level.
The same determination is made when adenoid hypertrophy generates frequent problems in breathing, sinusitis, rhinitis or constant episodes of high fever. In all these cases, an intervention is carried out that consists of scraping or removing the vegetations that protrude from the mucosa.
The ideal age for children to undergo this procedure is considered to be two years. When it comes to very frequent serious otitis, specialists proceed to intervene regardless of the age of the affected person.
In the cases of babies who are not yet one year old, the procedure that is applied is not properly an operation . The otolaryngologist crushes these tissues using his finger ; Afterwards, and depending on the evolution of these patients, it is evaluated if the intervention is necessary.

Adenoidectomy
This is the name given to the intervention by which the adenoid glands are removed. Generally, tonsillotomy – removal of the tonsils – is also performed alongside this procedure.
It is an outpatient operation, almost always applied to children, in which the patient receives general anesthesia. The little one will return home the same day and full recovery will take a maximum of two weeks.